Advancements in technology have continuously reshaped the world we live in, and the field of medicine is no exception. In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a groundbreaking concept, enabling seamless connectivity and communication between devices and people. One of the most remarkable applications of IoT in healthcare is the ability for surgeons in North America to remotely perform surgeries in Africa. This remarkable feat is transforming the landscape of healthcare delivery, bridging geographical gaps, and providing life-saving interventions to patients who might not otherwise have access to specialized surgical care. In this blog post, we will delve into how IoT is making remote surgeries a reality, its benefits, and the challenges that need to be addressed.
The Role of IoT in Remote Surgeries:
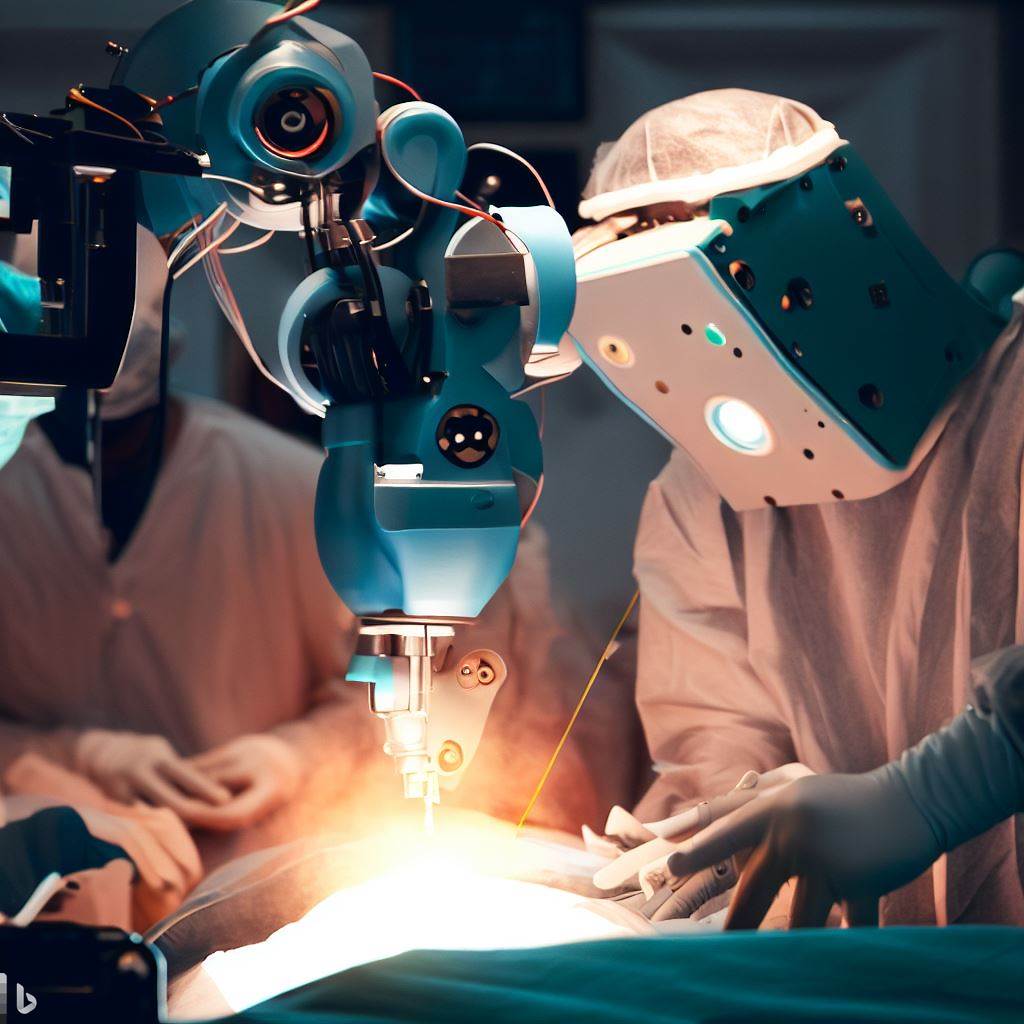
IoT technology has made it possible for surgeons to perform surgeries in remote locations through the integration of high-speed internet, robotic systems, and real-time data transmission. The concept of remote surgery, also known as telesurgery or telesurgery, involves a surgeon controlling robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments from a distant location. The surgeon’s movements are captured, transmitted, and replicated by the robotic arms, providing the necessary precision and dexterity required for complex surgical procedures.
IoT devices, such as wearables and sensors, play a crucial role in remote surgeries. These devices enable the collection and transmission of real-time patient data, including vital signs, imaging results, and surgical site information. Surgeons can access this data remotely, ensuring they have comprehensive information to make informed decisions during the surgical procedure. Furthermore, IoT facilitates seamless communication between the surgical team in North America and the on-site medical staff in Africa, promoting collaboration and coordination throughout the surgery.
Benefits of Remote Surgeries in Africa:
The introduction of remote surgeries in Africa brings numerous advantages, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized healthcare services. Here are some notable benefits:
- Improved Accessibility: Remote surgeries eliminate the need for patients to travel long distances or even cross borders to receive specialized surgical care. This is especially beneficial in rural and underserved areas where healthcare facilities are scarce.
- Enhanced Surgical Expertise: By connecting African hospitals with skilled surgeons from North America, remote surgeries provide access to advanced surgical techniques and specialized knowledge that may not be readily available locally. This results in better patient outcomes and an increase in the overall quality of healthcare in the region.
- Reduced Costs and Time: Remote surgeries minimize the financial burden on patients who would otherwise need to incur significant expenses for travel, accommodation, and post-operative care. Moreover, these surgeries can be performed promptly, reducing the waiting time for critical procedures and potentially saving lives.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the concept of remote surgeries holds immense promise, several challenges must be addressed to ensure its successful implementation:
- Reliable Internet Infrastructure: Stable and high-speed internet connectivity is crucial for transmitting real-time data and ensuring uninterrupted communication between surgeons and on-site teams. Adequate infrastructure is essential to overcome connectivity issues that might impede the success of remote surgeries.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data and ensuring its confidentiality is paramount. Robust security measures must be implemented to safeguard sensitive medical information from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Technical Training and Support: Both the surgical teams in North America and the on-site medical staff in Africa require comprehensive training to effectively operate the robotic systems and IoT devices. Ongoing technical support and skill development programs are necessary to address any operational challenges that may arise.
Conclusion:
The convergence of IoT and remote surgery is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized surgical care, such as Africa. Through this transformative technology, North American surgeons can remotely perform complex surgeries, providing patients in Africa with life-saving interventions and improving overall healthcare outcomes. However, it is crucial to address the challenges of infrastructure, data security, and technical training to ensure the widespread adoption and success of remote surgeries. With continued advancements in IoT and a collaborative global approach, we can truly revolutionize healthcare, bridging geographical barriers and bringing quality medical interventions to those who need them most.